Automotive DMS for OEMs and Dealerships
The Most Powerful Vehicle Management System
Industry’s most intelligent and data-driven Dealership Network Management System, built for automotive retailers. It combines modern technology, scalable architecture, and customer-focused automation with advanced analytics and AI-powered insights to drive meaningful growth.
Streamline operations, boost efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences across your entire dealership channel network with our AI-powered DMS platform built specifically for dealer and service network, Electric Vehicles segment, and heavy equipment, EV segment and heavy industrial machinery sellers.




Automotive Dealer Management for OEMs and Dealerships
Elevate your dealerships performance with Intelligent automation, AI-driven insights, streamlined operations, and exceptional customer experiences.
Excellon Automotive DMS reimagines how OEMs and dealerships manage their operations, integrating sales, service, inventory, and customer engagement into a seamless, agile platform. Our DMS empowers you to take sales and after-sales strategies to the next level.
By leveraging AI-driven insights, we simplify complexities and enhance growth throughout the distribution ecosystem, helping dealerships and OEMs thrive in an evolving market.
200 Million+
10,000+
98%
25 Million+
Vehicles sold through Excellon platform
40%
100%
Vice President, Sales & Customer Care
Mahindra 2-Wheelers Limited
Vice President, Sales & Customer Care Mahindra 2-Wheelers Limited
All-in-one DMS for the automotive and industrial sectors
Sales Management with CRM
Transform your sales operations with our AI-powered CRM that streamlines lead management, automates follow-ups, and provides predictive insights for higher conversion rates. Our integrated solution ensures seamless collaboration between sales teams and delivers personalized customer experiences at scale.
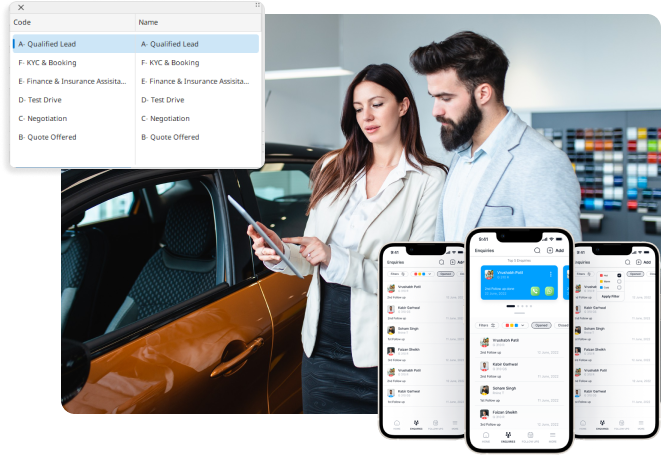
End-to-end sales cycle management
Leads and campaigns management
Lead to quote
Predictive demand forecasting and planning
Integrated call center
AI-driven test drives to bookings conversions
Intuitive mobile app for sales
Empower your salesforce with an intuitive mobile app that provides real-time data, customer information, and sales tools on the go.
AI-powered recommendations
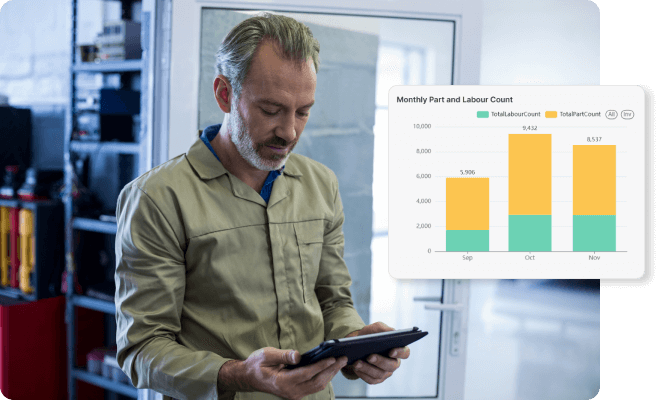
Comprehensive service and workshops management
Ensure your service department delivers an exceptional experience by providing real-time scheduling, job order creation, and AI-powered service efficiency recommendations. Our service management module ensures minimal downtime and maximizes customer satisfaction.

Service appointments scheduling
AI-powered repair job order creation
Estimates, claims and warranty management
Automated service bay and technician allocations
Automated customer reminders and communications
Integrated technician mobile app
AI-powered recommendations for service efficiency
Empower your salesforce with an intuitive mobile app that provides real-time data, customer information, and sales tools on the go.
Smart inventory and spare parts management
Keep your inventory lean and responsive with real-time tracking, AI-driven replenishment, and integrated parts warehouse management. Optimize your stock to ensure you have the right parts and vehicles at the right time, avoiding overstocking or shortages.
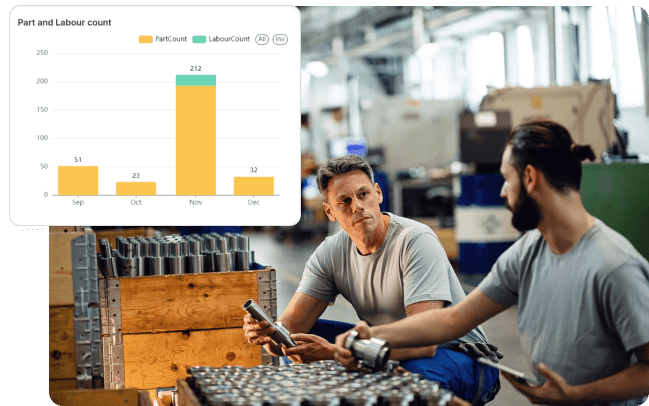
Vehicle inventory management
AI-powered vehicle planning and ordering
Spare parts warehouse management
Parts purchase planning and auto ordering
Stock classification, adjustment and valuation
AI-driven intelligent parts ordering
Inventory movement and trending analysis
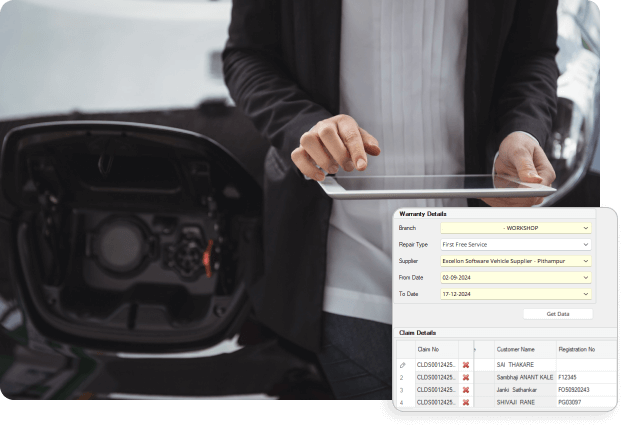
Efficient warranty and claims
Streamline your warranty and claims processes with an integrated solution that ensures quick processing, transparency, and customer satisfaction. Our AI-powered warranty management system reduces manual effort and ensures claims are processed accurately.

Centralized warranty management
Warranty claim process automation
Claims validations and approvals
Across dealerships warranty claims insights
AI-driven warranty claims analysis
Warranty parts ordering and returns
AI-powered recommendations for service efficiency
Agile pricing and promotions
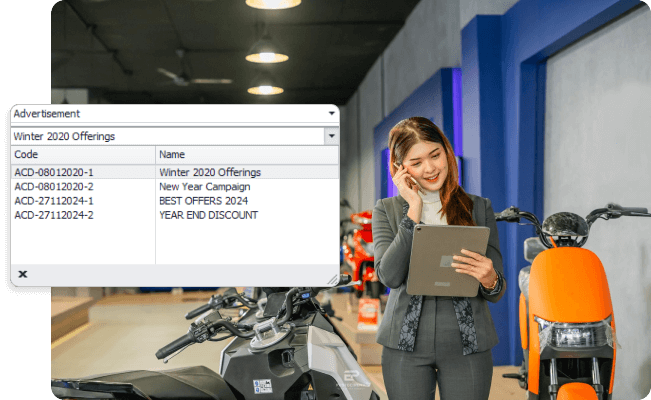
Centralized pricing management
National and regional promotions management
Dealer-specific promotions and incentives
Dynamic pricing algorithms with real-time price adjustments
Targeted promotions and offers
Market trends, demand and price sensitivity insights
AI-powered pricing and promotion recommendations
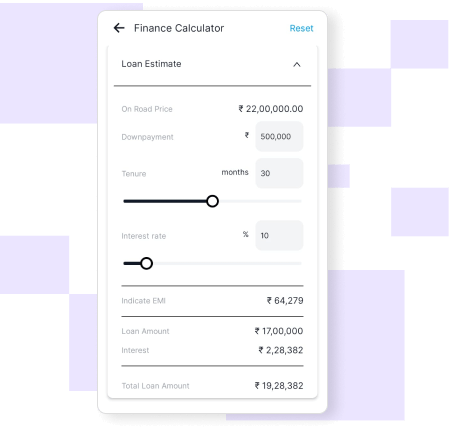
Finance and accounting management
Optimize financial operations and ensure compliance with a fully integrated finance and accounting solution. Our finance module simplifies processes such as invoicing, payments, and cash flow management while providing real-time financial insights.

Budgeting and financial planning
Sales and revenue management
Digital invoicing and payments processing
Cashflow management
Get insights into warranty claims across your entire dealership network to identify trends and issues.
Reconciliation and banking
Accounts receivables and payables
Dealership financials
Get a complete overview of your dealership’s financial status in real-time.
Audit and compliance
Ensure compliance with financial regulations using built-in audit tools.
AI-powered financial health analysis and recommendations
Use AI to assess financial health and receive actionable recommendations.
Growth-centric analytics and insights
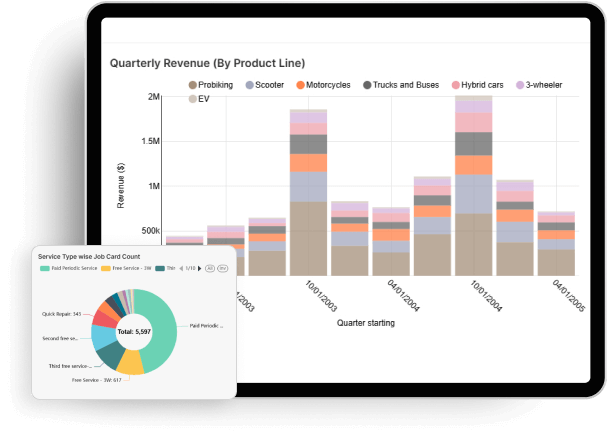
Real-time in-platform 360-degree insights
ETBR reporting and insights
Intuitive dashboards and reports
PerformancePulse
SalesPulse
ServicePulse
FinancePulse
Track financial health and cash flow to keep your dealership profitable by closely monitoring revenue, expenses, and profit margins, ensuring that your financial operations remain sound and sustainable.
OperationsPulse
Get insights into operational efficiency, helping identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and ensure that dealership’s day-to-day activities are optimized for maximum productivity and profitability.
AI-driven predictions and recommendations
Leverage our powerful ExcellonPulse AI engine to predict future trends, such as sales performance, customer preferences, and service demands, while receiving actionable recommendations that help your dealership take proactive steps towards sustainable growth and enhanced customer satisfaction.

Customer delight
Create delightful customer experiences at every interaction point, from initial inquiry to post-purchase. Our customer-centric tools ensure that customers are engaged and satisfied at every stage of their journey.

Lead to sales and post-sales customer relationships management
Customer self-service portals
Virtual showrooms and digital experiences
Post-purchase engagement & loyalty programs
AI-driven personalisation
Accounts receivables and payables
High-touch customer engagement and communications
Sentiment analysis and engagement recommendations
Seamless Integration
Excellon DMS delivers seamless integration across your entire automotive retail ecosystem, creating a unified digital backbone that connects OEMs, dealerships, and customers. Our platform’s native integration capabilities enable real-time synchronization with OEM central systems for vehicle allocation, parts catalogs, and warranty processing, while simultaneously connecting your dealership’s core operations – from sales and service to parts and finance.
This comprehensive integration eliminates data silos, automates cross-system workflows, and ensures consistent information flow across manufacturer portals, dealer management tools, diagnostic systems, financial platforms, and customer touchpoints, ultimately driving operational efficiency and delivering superior customer experiences.



